Introduction
When it comes to maintaining good oral health, dental X-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating dental problems. They provide dentists with valuable insights that cannot be obtained through a regular dental examination alone. In this article, we will explore the world of dental X-rays, uncovering the hidden truths behind their importance, safety, types, and benefits.
Table of Contents
- Why Dental X-Rays Matter
- The Safety of Dental X-Rays
- Types of Dental X-Rays
- Benefits of Dental X-Rays
- How Dental X-Rays Are Taken
- Interpreting Dental X-Ray Images
- Frequency of Dental X-Rays
- Special Considerations for Pregnant Women
- Pediatric Dental X-Rays
- Dental X-Rays and Oral Health Conditions
- Digital Dental X-Rays vs. Traditional Film X-Rays
- Minimizing Radiation Exposure
- Common Misconceptions about Dental X-Rays
- The Future of Dental Imaging
- Conclusion
Why Dental X-Rays Matter
Dental X-rays are an essential tool that helps dentists diagnose dental issues that may not be visible during a regular examination. They allow dentists to detect cavities, evaluate the health of the tooth roots, check for bone loss, assess the condition of the jawbone, and identify any abnormalities or infections.
The Safety of Dental X-Rays
Dental X-rays are considered safe and are accompanied by minimal radiation exposure. The advancements in technology and the use of digital X-rays have significantly reduced radiation levels compared to traditional film X-rays. Additionally, dentists take necessary precautions such as using lead aprons and thyroid collars to protect patients from radiation exposure.
Types of Dental X-Rays
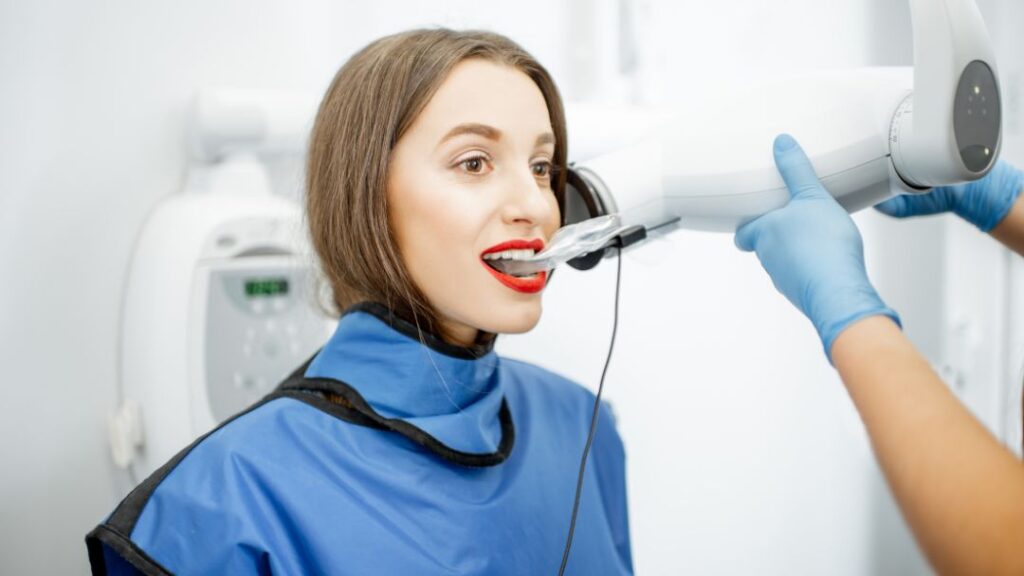
There are several types of dental X-rays commonly used in dental practices:
1. Bitewing X-Rays
Bitewing X-rays are used to detect cavities between the teeth, check the fit of dental restorations, and assess overall oral health.
2. Periapical X-Rays
Periapical X-rays capture the entire tooth, including the root and surrounding bone. They help dentists identify dental infections, abscesses, and abnormalities.
3. Panoramic X-Rays
Panoramic X-rays provide a broad view of the entire mouth. They are helpful in assessing the development of teeth, evaluating the jaw joint, and detecting any impacted teeth.
4. Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
CBCT scans provide three-dimensional images of the teeth, jawbone, and surrounding structures. They are particularly useful for planning dental implant placements, orthodontic treatments, and diagnosing complex dental issues.
Benefits of Dental X-Rays
Dental x-rays offer numerous benefits that contribute to effective dental care:
- Early Detection of Dental Problems: X-rays help identify dental issues in their early stages, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing further complications.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Dental x-rays provide dentists with detailed information about the patient’s oral health, enabling them to develop personalized treatment plans.
- Monitoring Dental Development: X-rays assist in monitoring the growth and development of teeth, especially in children.
- Improved Accuracy: X-rays enhance the accuracy of dental procedures, ensuring precise diagnoses and successful treatments.
- Enhanced Patient Education: X-rays allow dentists to visually explain dental conditions to patients, facilitating better understanding and informed decision-making.
How Dental X-Rays Are Taken
Dental x-rays are taken in dental offices using specialized x-ray machines. The process is quick and painless. The patient wears a lead apron to protect the body from radiation, and the x-ray technician positions the x-ray film or digital sensor inside the mouth to capture the images.
Interpreting Dental X-Ray Images
Interpreting dental x-ray images requires expertise and training. Dentists analyze the images to identify dental issues, assess the severity of problems, and determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Frequency of Dental X-Rays
The frequency of dental x-rays depends on individual factors such as age, oral health condition, and risk of dental problems. Generally, adults may require x-rays every 1 to 2 years, while children may need them more frequently to monitor their dental development.
Special Considerations for Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should inform their dentist about their pregnancy. Although dental x-rays are generally safe, dentists may take additional precautions or postpone non-emergency x-rays until after childbirth to minimize radiation exposure.
Pediatric Dental X-Rays
Pediatric dental x-rays are essential for monitoring the growth and development of children’s teeth. Dentists carefully consider the necessity of x-rays for children and use low radiation settings to minimize exposure.
Dental X-Rays and Oral Health Conditions
Dental x-rays play a crucial role in diagnosing various oral health conditions, including:
- Tooth decay and cavities
- Gum disease
- Dental abscesses
- Bone loss
- Tumors and cysts
Digital Dental X-Rays vs. Traditional Film X-Rays
Digital dental X-rays have revolutionized dental imaging. They offer several advantages over traditional film X-rays, including:
- Reduced radiation exposure
- Instant image availability
- Enhanced image quality
- Easy storage and transfer of images
- Environmentally friendly (no need for film development)
Minimizing Radiation Exposure
Dentists follow strict guidelines and use advanced techniques to minimize radiation exposure during dental X-rays. These include using lead aprons, collimators to focus the X-ray beam, and digital sensors that require less radiation than film.
Common Misconceptions about Dental X-Rays
There are a few common misconceptions about dental X-rays that need clarification:
- Dental X-rays do not cause cancer. The radiation levels in dental X-rays are very low and pose minimal risk.
- Lead aprons and thyroid collars protect patients from radiation exposure during X-rays.
- Digital X-rays emit significantly less radiation than traditional film X-rays.
The Future of Dental Imaging
The field of dental imaging continues to advance rapidly. New technologies, such as 3D imaging and artificial intelligence, are revolutionizing the way dentists diagnose and treat dental problems. These advancements will further enhance the accuracy, efficiency, and safety of dental imaging procedures.
Conclusion
Dental x-rays are an indispensable tool in modern dentistry. They provide valuable insights, aiding in the early detection and treatment of dental issues. With advancements in technology and safety measures, dental x-rays are now safer and more effective than ever before. By embracing dental X-rays, patients can enjoy better oral health and a brighter smile.
FAQs
- Are dental X-rays necessary for routine check-ups?
Yes, dental X-rays are necessary for routine check-ups as they help dentists identify dental problems that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Do dental X-rays expose patients to harmful radiation?
Dental X-rays expose patients to minimal radiation, and dentists take necessary precautions to minimize exposure.
- Can pregnant women undergo dental X-rays?
Pregnant women can undergo dental X-rays, but dentists may take additional precautions to minimize radiation exposure.
- How often should dental X-rays be taken?
The frequency of dental X-rays depends on individual factors such as age, oral health condition, and risk of dental problems.
- How do digital dental X-rays differ from traditional film X-rays?
Digital dental X-rays offer advantages such as reduced radiation exposure, instant image availability, and enhanced image quality compared to traditional film X-rays.